Setting up SSH tunnel is an effective solution, for example, if you want to log into the remote database in a secure way. Thanks to the SSH tunnel, you can set up a remote service on your computer's local port.
The following tutorials assume, that the server has already configured key authentication via SSH.
How to set up an SSH tunnel in Windows
- Download the putty.exe application and run it. In the window that will appear on the left, drop down Connection > SSH and select "Tunnels".
- In the "Add new forwarded ports" section, fill the fields:
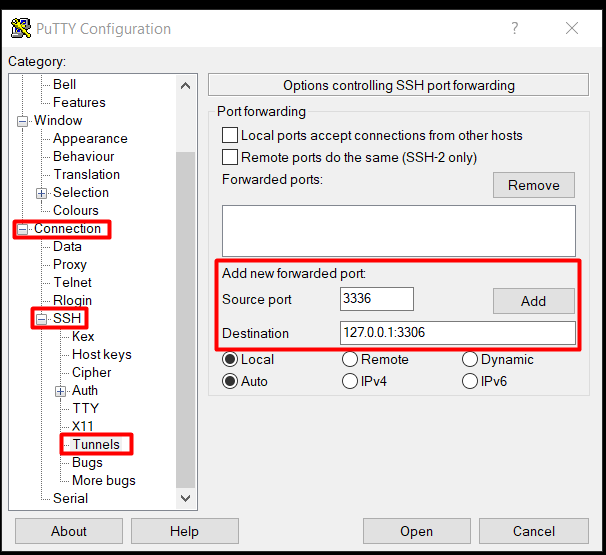
- Source port - number of the local port you want to use (in the example it will be 3336),
- Destination - enter 127.0.0.1:SERVICEPORT (in the example it will be 3306).
- Click the "Add" button.
- Then, on the left side, again drop down Connection > SSH and select "Auth".
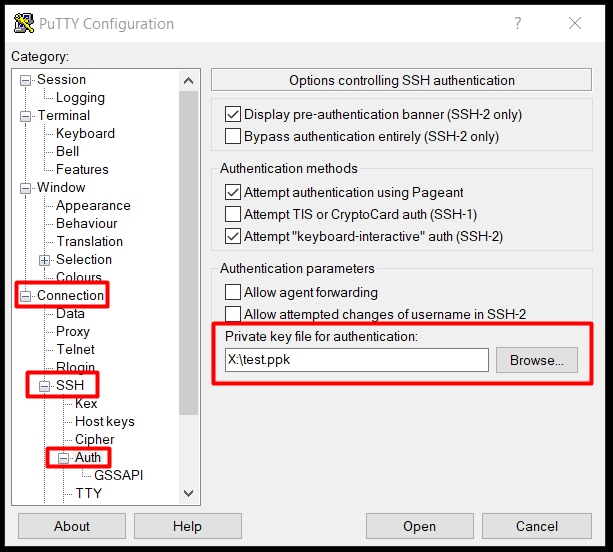
In the "Private key file for authentication" section, set path to private key. - Then, on the left side of the page, we again expand Connection and select "Date".
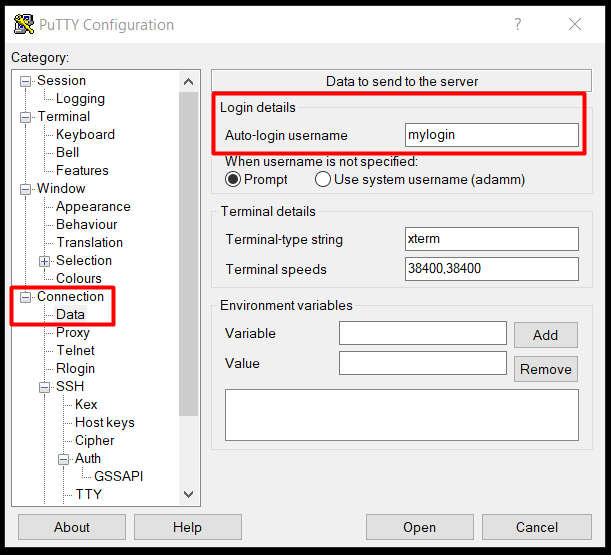
In the Login Details section we will complete the "Auto-login username" field with the SSH user name to which we will connect. - Then select "Sessions" on the left side.
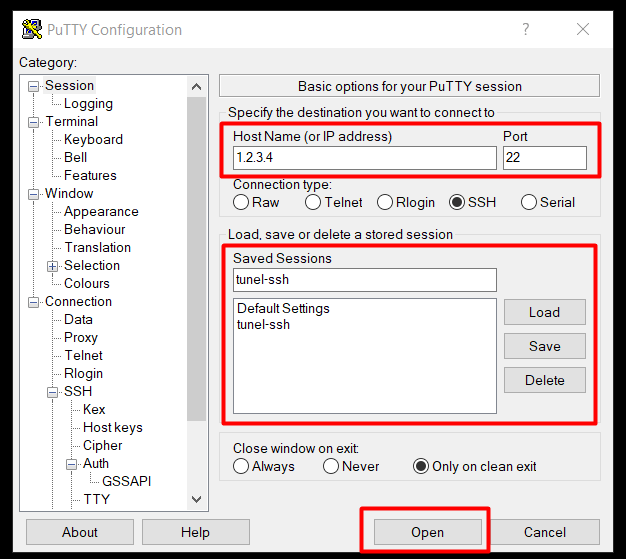
Fill in the fields accordingly:- Host name - let's give the IP address of the remote server or the domain that is directed to it,
- Port - enter the port number under which SSH operates - by default it is 22, but if server is managed by us it will be 7324,
- Saved Sessions - provide a session name.
- Click "Save" to save the session for the future.
- Click "Open" to open the session and set up the SSH tunnel.
In the window that will appear with the console, we recommend running the >top command, so that it does not break the set session. To exit the top, press the q key.
How to set up the SSH tunnel in MacOS/Linux
Below tutorial is made for mysql/mariadb connection, but service can be changed based on needs.
- Open the terminal and then enter the command:
ssh -N -L LocalPort:127.0.0.1:ServicePort -p SSHPort MyLogin@RemoteHost
where:- LocalPort - number of the local port you want to use (in the example it will be 3336),
- ServicePort - port service number on which service is listening,
- SSHPort - port on which ssh listen on remote host,
- MyLogin - my ssh username,
- RemoteHost - IP or domain name, of remote host with service.
- Now we need to test SSH tunnel, so open another terminal and enter:
mysql -h 127.0.0.1 --port=3336 -u DatabaseUser -p DatabaseName
where:- DatabaseUser - user which will be used to connect to database,
- DatabaseName - name of database to which we will be connecting.

